Is Caviar Halal?
Understanding Caviar
Caviar is a delicacy consisting of salt-cured fish eggs, typically from sturgeon species. The most prized caviar comes from the Caspian Sea and the Black Sea, where sturgeon have been harvested for centuries. The three main types of caviar are:
- Beluga: The most expensive and sought-after caviar, known for its large, soft eggs with a buttery flavor.
- Osetra: Slightly smaller eggs than Beluga, with a nutty, earthy taste and a golden to dark brown color.
- Sevruga: The smallest and most abundant caviar, with a strong, briny flavor and a gray to black color.
| Type | Egg Size | Color | Flavor Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beluga | Large | Light to Dark | Buttery, Delicate |
| Osetra | Medium | Golden to Dark Brown | Nutty, Earthy |
| Sevruga | Small | Gray to Black | Strong, Briny |
The Islamic Perspective on Caviar
In Islam, the concept of halal refers to anything that is permissible according to Islamic law. For a food item to be considered halal, it must meet certain criteria:
- The source animal must be halal (e.g., cow, sheep, goat, chicken, fish with scales)
- The animal must be slaughtered according to Islamic guidelines
- The food must not contain any prohibited ingredients (e.g., pork, alcohol)
When it comes to caviar, the main factor determining its halal status is the source of the fish eggs.
Fish in Islam
In Islam, fish are generally considered halal, as stated in the Quran:
“Lawful to you is game from the sea and its food as provision for you and the travelers…” (Quran 5:96)
However, there is a debate among Islamic scholars regarding which types of fish are permissible. The majority view is that only fish with scales are halal, while a minority opinion allows for the consumption of all aquatic animals.
Sturgeon and Scales
Sturgeon, the primary source of caviar, are a unique case when it comes to scales. While sturgeon have bony plates called scutes, they lack the typical overlapping scales found on most fish. This has led to differing opinions among Islamic scholars:
- The Majority View: Sturgeon are not considered to have scales and, therefore, are not halal. This opinion is held by the Hanafi, Maliki, and Hanbali schools of Islamic jurisprudence.
- The Minority View: Sturgeon scutes are considered equivalent to scales, making the fish halal. This view is supported by some scholars within the Shafi’i school of thought.
Processing and Additives
Even if the source of caviar is considered halal, the processing methods and additives used can affect its permissibility.
Traditional Processing
The traditional method of producing caviar involves harvesting the fish eggs, washing them, and then salt-curing them. Salt is the only additive used in this process, which is generally considered halal.
Modern Processing
Some modern caviar producers may use additional ingredients or processing aids, such as:
- Preservatives (e.g., borax)
- Flavor enhancers (e.g., MSG)
- Pasteurization
The halal status of these additives and processes must be evaluated on a case-by-case basis, as some may be derived from non-halal sources or involve the use of alcohol.
Fatawa on Caviar

Islamic legal rulings, or fatawa, have been issued by various scholars and institutions regarding the permissibility of caviar. While opinions may vary, the general consensus among contemporary Islamic authorities is that caviar from sturgeon is not considered halal due to the lack of scales on the fish.
Notable fatawa on the subject include:
- The Islamic Religious Council of Singapore: “Caviar is not halal because it comes from sturgeon, which is a scaleless fish.”
- The European Council for Fatwa and Research: “Sturgeon caviar is not permissible for consumption because sturgeon does not have scales in the Islamic legal sense.”
- The Assembly of Muslim Jurists of America: “The majority of scholars agree that sturgeon is not considered a fish with scales and, therefore, its caviar is not halal.”
Alternatives to Sturgeon Caviar
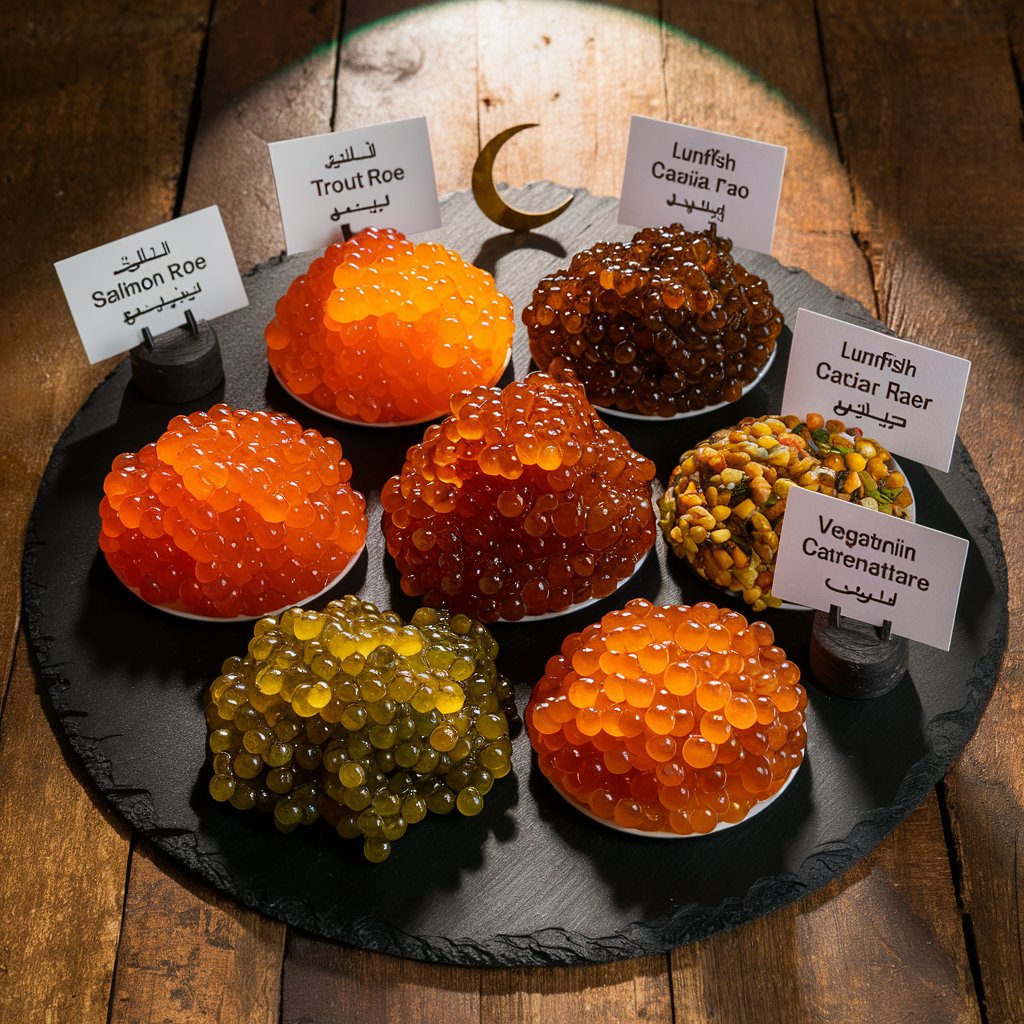
For Muslims who wish to enjoy the taste and texture of caviar without compromising their religious beliefs, there are several halal alternatives available:
- Salmon Roe: Salmon are a type of fish with scales, making their eggs (also known as ikura) halal. Salmon roe has a bright orange color and a slightly sweet, salty taste.
- Trout Roe: Like salmon, trout are a scaled fish, and their eggs are considered halal. Trout roe is smaller than salmon roe and has a milder flavor.
- Lumpfish Caviar: Lumpfish are a type of scaled fish found in the North Atlantic. Their eggs, often dyed black or red, are a popular and affordable alternative to sturgeon caviar.
- Vegetarian Caviar: Some companies offer plant-based caviar alternatives made from seaweed, algae, or other ingredients. These products mimic the appearance and texture of caviar while being suitable for halal diets.
Ensuring Halal Caviar
For Muslims who choose to consume caviar, it is essential to ensure that the product is sourced from a halal supplier. This involves verifying that:
- The fish eggs come from a scaled fish (e.g., salmon, trout, lumpfish)
- The processing methods and additives used are halal-certified
- The caviar is not processed or packaged alongside non-halal products
Reputable halal certification bodies, such as the Islamic Food and Nutrition Council of America (IFANCA) and the Halal Food Authority (HFA), can provide guidance and assurance on the halal status of caviar products.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the halal status of caviar is a complex issue that depends on various factors, including the source of the fish eggs, the processing methods, and the Islamic legal rulings on the matter. While the majority view among Islamic scholars is that sturgeon caviar is not halal due to the lack of scales on the fish, there are alternative options available for Muslims who wish to enjoy the taste and texture of caviar.
By understanding the principles of halal food and seeking guidance from trusted Islamic authorities, Muslims can make informed decisions about the permissibility of caviar in their diets. Ultimately, the decision to consume caviar or any other food item is a personal choice that should be based on one’s religious beliefs, knowledge, and conscience.